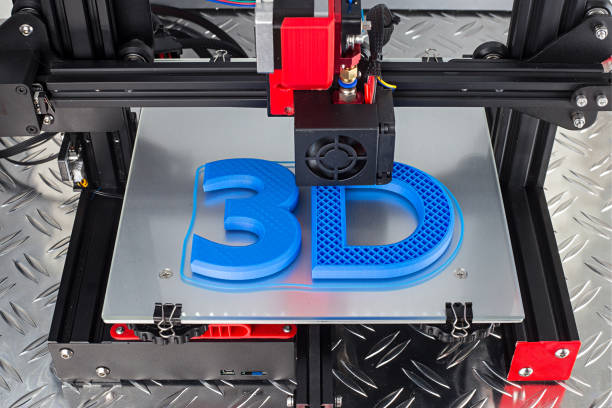
Few inventions in the field of technological wonders have captured our attention quite like 3D printing. Known by another name, additive manufacturing, this ground-breaking technology has transformed a number of industries, including aerospace and healthcare, by enabling the layer-by-layer construction of three-dimensional items from digital models.
We explore the complexities of 3D printing in this essay, as well as its uses, benefits, and significant influence on our daily lives.
Understanding 3D Printing:
Fundamentally, 3D printing is building objects one layer at a time using digital plans. 3D printing adds material layer by layer, which makes it a more effective and adaptable process than traditional subtractive manufacturing techniques that entail cutting away from a solid block of material.
Usually, the procedure starts with the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a digital model. The 3D printer uses this model as a blueprint once it has been cut into thin cross-sectional layers. The printer then complies with these directives, adding material layer by layer until the desired item is formed by their fusion.
How 3D Printing Works:
In 3D printing, a variety of processes are employed, each with its own special methodology and materials. Several of the most popular techniques are as follows:
1- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Using this technique, thermoplastic filaments are heated and then forced through a nozzle to build layers. FDM is a popular technology for creating inexpensive plastic parts and for quick prototyping.
2. Stereolithography (SLA): SLA is a process that creates complex, finely detailed items by layering and curing a vat of liquid resin using a UV laser. It’s frequently used in applications where excellent surface quality and precision are necessary.

3. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): In SLS, powdered materials like ceramic, metal, or plastic are fused together layer by layer to create solid objects using a powerful laser.This process is well known for its capacity to create intricate geometries and useful components.
Benefits of 3D Printing:
Because of its versatility, 3D printing has many uses and benefits in a variety of fields.
1 – Rapid prototyping: By allowing designers and engineers to test and iterate ideas fast, 3D printing helps to drastically cut down on development time and expenses.
2 – Customization: The ability to make individualized products, such as consumer goods, dental implants, or bespoke prosthetics, is one of the most alluring features of 3D printing.
3 – Complex Geometries: Producing complex forms and geometries is a challenge for traditional production techniques. In this sense, 3D printing shines, making it feasible to fabricate complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to accomplish in other ways.
4 – On-Demand Manufacturing: Large stockpiles and waste can be avoided by producing items on demand using 3D printing. This versatility is especially useful in sectors where customization and fast response times are essential, such as aerospace and healthcare.
Why We Need 3D Printing:
Numerous variables, such as the following, are driving the adoption of 3D printing:
1. Innovation: 3D printing encourages innovation by giving people and organizations the freedom to experiment with new ideas and push the envelope of imagination.
2. Efficiency: 3D printing provides a more economical and environmentally friendly substitute for conventional manufacturing techniques by optimizing the production process and cutting down on material waste.
3. Accessibility: As 3D printing technology has become more widely available, new paths for economic growth and opportunities have opened up for hobbyists, small enterprises, and entrepreneurs.
4-Advancing Industries: 3D printing is propelling developments in a number of industries, including healthcare and automotives. It is enabling the creation of medical implants customized for individual patients as well as the production of lightweight, fuel-efficient aeronautical components.
How Can I make it?
1. Get a 3-dimensional printer:
Find a 3D printer that meets your needs and price range by doing some research. There are several kinds out there, from low-cost desktop printers to high-end industrial devices. Or you can contact with 3D Studios which they already have the materials. So your cost will be low.
For Printing 3D Studio we would suggest contact with NULL STATION and also there is others studios are available too.
When making your choice, take into account elements like build volume, resolution, material compatibility, printing technology (FDM, SLA, SLS), and build volume.
3D printers can be bought directly from manufacturers, from specialty shops, or via internet vendors.
2. Learn the Basics:
Read beginner’s manuals, attend online tutorials, and participate in community forums to become familiar with the principles of 3D printing.
Recognize the fundamental ideas behind things like CAD modeling, slicing software, printer calibration, and filament types. Or if you don’t want any hessl ethen contact with NULL STATION. One of the reliable 3d animation studio in Bangladesh providing 3D Print model support
3. Select Design Software:
You have two choice either create by it yourself or hire 3D Studio Like Null Station. Now To develop your 3D models, choose a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) program. Popular choices include Blender, Fusion 360, SolidWorks, Tinkercad (beginner-friendly), and SolidWorks.
Before taking on more difficult projects, study tutorials and practice making basic designs to enhance your skills.
4. Prepare Your Designs:
After creating or downloading a 3D model, prepare it for printing using slicing software such as Cura, Simplify3D, or Slic3r.
Depending on the desired result and the characteristics of the material, change parameters like layer height, infill density, and print speed.
5. Original Source Documentation:
Obtain the right printing materials (resins or filaments) for the printer and applications that you have selected.
PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU are common filament kinds; each has special qualities and can be used for a variety of projects.
Select from a range of photopolymer resins designed for particular uses, including conventional, flexible, and high-temperature resins, if you use a resin-based printer.
6. Begin Printing:
Open the 3D model file in the slicing program and produce the G-code, which gives the printer instructions.
Depending on the capabilities of your printer, you can link the G-code file to it using Wi-Fi, an SD card, or a USB connection.
Before beginning your print, make sure the bed is level, the filament or resin is loaded, and the printer is calibrated according to the setup instructions.
To maximize print quality and dependability, keep an eye on the printing process and make any necessary adjustments.
7. Post-Processing and Finishing:
After the print is finished, carefully take it off the build platform and, if necessary, take down any support structures.
To improve the look and surface quality of your print, think about using post-processing methods like painting, sanding, or vapor smoothing, depending on the material and desired finish.
8. Iterate and Experiment:
As you get more comfortable with 3D printing, welcome the process of iteration and experimentation. To increase your abilities and originality, don’t be scared to experiment with different designs, materials, and methods.
Connect with other 3D printing aficionados, exchange advice and pointers, and show off your creations by joining online communities and forums.
Not all 3D printers are created equal: Exploring different printing methods
3D printers are like superheroes – they have special powers! But just like each superhero has a unique way of saving the day, different 3D printers use different methods to bring your ideas to life. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common types:
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling):
FDM printers work similarly, melting plastic filament and squeezing it out to form your object. They’re popular for beginners because they’re affordable and easy to use, although the prints might not be super smooth.
SLA (Stereolithography):
Think of a laser making tiny puddles of light on a vat of liquid. SLA printers use a laser to cure (harden) special resin one layer at a time, creating very smooth and detailed objects. They’re great for intricate designs like jewelry or figurines, but the materials can be more expensive.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering):
SLS printers use a laser to fuse powdered materials like plastic, metal, or even glass! They can create strong and complex objects, perfect for prototypes or even functional parts. However, SLS printers are typically for industrial use because they can be quite costly.
This is just a glimpse into the exciting world of 3D printing methods! Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, so the best type for you depends on your project and budget.
Conclusion:
In summary, 3D printing is a manufacturing paradigm change that offers unmatched flexibility, efficiency, and innovation. Its pivotal role in the Fourth Industrial Revolution stems from its exceptional precision and speed in converting digital designs into tangible items. With 3D printing, the possibilities are almost endless as the technology develops and matures, pointing to a future where creativity, sustainability, and customisation will rule supreme.
FAQs
What can I actually print with a 3D printer?
The possibilities are almost endless! You can print toys, phone cases, prototypes for inventions, custom tools, decorative objects, prosthetics, architectural models, and even some food items (with special printers).
2. How much does a 3D printer cost?
Prices vary depending on features and capabilities. Beginner printers can start around $200, while professional models can cost tens of thousands.
3. Is 3D printing safe?
Generally, yes. However, some materials used in 3D printing may release fumes, so proper ventilation is important. Always follow the manufacturer’s safety instructions.
4. Do I need to be a tech whiz to use a 3D printer?
Not necessarily! Many printers come with user-friendly software, and there are plenty of online tutorials and resources to get you started. However, more advanced techniques might require some learning.
5. Where can I find 3D models to print?
There are many online repositories where you can download free or paid 3D models (.stl files) for printing. You can also find communities where people share their own creations.
6. Can I design my own 3D models for printing?
Absolutely! There are various 3D design software options available, some even free and beginner-friendly.